Manual Strobe Control
1. Guide numbers, strobe power, and the Guide Number formulaWhen you can't rely on TTL strobe control, what are your alternatives? Manual control is really the only other way to control your strobe. So let's jump right in. Here's the basic situation: your strobe dumps all of its light while the shutter is open. There's no other way the system can work. Click here if you want to know why. So how can you control how much light reaches the film from your strobe? Basically, there are three ways. One way is with your lens aperture. You have to set the shutter speed for a range that syncs with the strobe, but the aperture is completely under your control. The smaller the aperture, the less strobe light gets to the film. The second way is by changing the distance between you and your subject. I don't know if you remember high school physics or not, but the intesity of light falls of like the square of the distance from the source. The same applies to your strobe light. If you take a picture from twice as far away, your strobe will have one quarter the effect. Three times farther away? One ninth the effect. You get the idea. So you can change the distance between you and your subject to change the effect of the strobe. The third way is possible only with more complex and expensive strobes: you can dial back the strobe power. Some strobes come with a knob where you set how much light you want from the strobe: full power, 1/2 power, 1/4 power, 1/8 power, etc. But let's ingore that power dial for a minute, and pretend that we have a fixed-power strobe. How do we know what aperture and shutter speed to use for any given picture? First of all, forget the shutter speed for now. As long as it's within the sync speed range for your camera, you'll be OK. Then how do we know what aperture to use? The answer is to use a formula that applies to all strobes, and a number called the Guide Number (GN). The guide number for your strobe should be stated by the manufacturer. If the manufacturer is Ikelite, that Guide Number will probably be reliable. If the strobe was made by someone else, you'll probably have to take their guide numbers with a grain of salt; my experience is that many manufacturers over-rate their guide numbers, sometimes dramatically. This is probably a marketing ploy. The guide number is a number that tells you what aperture setting to use for the strobe-to-subject distance of your picture (or vice versa). The formula is GN = aperture * distance. The higher the guide number, the stronger the strobe. For example, the guide number for my Ikelite SubStrobe 200 is around 40, in feet for ISO 100 film. The GN for my Ikelite SubStrobe 50 units is 28. Why is the guide number for the SS-200 only 1.4 times as much as the GN for the SS-50, when the SS-200 is supposedly 4 times as powerful as the 50? Because the 50 concentrates its light into a relatively narrow cone with an opening angle of around 70 degrees. The SS-200 spreads its light out into a 100-degree cone. That means the 200 can "cover" a much wider lens than the 50. Since you've got more area to cover, the effective brightness of the light goes down. So how do we use the Guide Number formula? How about I show you some examples. In all the examples below, let's just assume I'm using my SS-200, with a guide number of 40. Its actual guide number is 38, but 40 makes for easier calculating. Let's say my subject is 5 feet from my strobe. To calculate the proper aperture, I re-arrange the GN formula from above like this: aperture = GN / distance. Now I solve for the aperture: aperture = 40/5 or f/8. If the subject is 3 feet, I set it to 40/3 = f/13. Now f/13 isn't a regular stop, so I'd shoot one at f/11 and another at f/16, and hope for the best. But what if I have set my aperture to some value (say, for proper background exposure, or depth of field, or whatever) and I don't want to re-set that? Can I use the guide number formula to tell me what distance I need to be from the subject? Sure, but I need to re-write the formula again: distance = GN / aperture. Let's try another example. Let's say I've picked 1/60 sec and f/8 for my exposure settings. I have the same GN 40 strobe. Where do I need to be relative to the subject? Use the formula: distance (in feet) = 40/8 = 5 feet away. If I had my aperture set to f/11, I'd need to close in to 40/11 = 3.6 feet. There's an easy way to remember all of this: if you have the aperture, divide it into the guide number to get your distance. If you have the distance, divide that into the guide number to get an aperture. Hey, wait a second! In the section on setting shutter speeds and apertures, we talked about how you have to set both of them in order to get a good exposure. Why are we only talking about apertures in this section on strobes? Doesn't the shutter speed have something to do with it? No. As long as the shutter speed is in the strobe sync range for your camera, the shutter speed is irrelevant as far as the strobe goes. If you really want to know why, click here. Are we clear on how to use the guide number? Then let's look at how to adjust the guide number for other situations than feet and 100-speed film. 2. Adjusting the GN formula for metric system or different film speedsWhy do manufacturers say things like "in feet for ISO 100 film" when they give you a guide number? Because of the guide number formula. Let's think about the GN-40 strobe we've been using all along. If I used a GN of 40 and told you the answer was in meters, what would happen? Well, you'd do that last calculation and decide that the right distance was 3.6 meters. Uh, converts to 11.7 feet, when we know the right answer was 3.6 feet. If you want to think in meters, you need the guide number in meters. For my SS-200, the guide number in meters is 12. Do that last calculation, and you'd get the proper distance as 12/11 = 1.09 meters. Get out your calculator; 1.09 meters = 3.53 feet, which is pretty close to 3.6 feet.. Aha! Now we're on to something. We didn't change the strobe, so the subject distance shouldn't change, no matter what distance units we use. But then the guide number has to change, right? Cool. Converting a "feet" guide number to "meters" is pretty simple: divide the "feet" guide number by 3.25 and you'll get the "meters" guide number. If you have a metric guide number and want it in feet, multiply by 3.25. What about film speed?If you switch from 100 speed film to 200 speed film, you need half the light, right? So if I set my distance & aperture based on the guide number for 100 speed film but I'm using 200 speed film, I'll get twice the light I need, right? And that's bad, right? So how do we fix it? I don't want to get into the long hairy explanation (you can read it here if you really care), but the solution is to multiply the guide number by the square root of 2 (i.e. 1.4) each time you double film speed. Alternatively, you can multiply the guide number by the square root of the ratio of the two film speeds in question. That's probably easier to remember. Want an example? OK, let's do the 5-foot subject distance example at ISO 200. Our old guide number was 40. Our new guide number will be 40 * sqrt(200/100) = 40 * 1.4 = 56. Then we apply the GN formula, so that a 5-foot-distant subject would then imply an aperture of 56 / 5 or f/11. Is that right? Sure. We had f/8 before, with 100 speed film. With 200 speed film, we need half the light. Thus we need to increase our aperture number by one stop, which decreases the light reaching the film by half, which is our actual goal. So what's one stop "down" from f/8? Look on your camera: it's f/11. Bingo! Another example? OK, what if we went to ISO 50 film? Then the new GN is 40 * sqrt(50/100), or 40 * 0.707 = 28. Then at 5 feet, we'd need an aperture of 28 / 5 = 5.6, or f/5.6. What's one stop more light than f/8? That's right: f/5.6. 3. Guide numbers in practiceAll of this is awfully complicated. How does your average mortal do these calculations under water, while setting up a photo? I have no idea; I'm not your average mortal. :) Seriously, that's way too much math to do underwater. No one does that. Strobes come with an exposure chart that allows you just to look up the answer on the chart. Match up film speed, strobe power setting, and distance, and the chart tells you aperture.
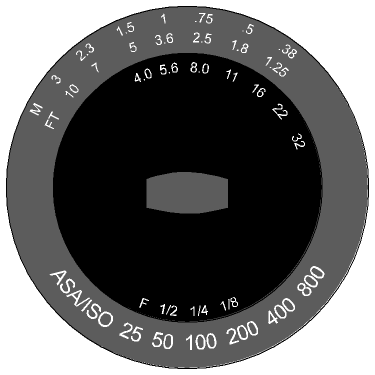
My Ikelite SubStrobe 200 has a rotating wheel on the back of the strobe (fig. 1). You line up the strobe power setting over the film speed you're using, and look on the other side of the wheel for aperture/distance combinations that will work. For instance, at quarter power and ISO 100 film, my SS 200 wheel tells me these combinations will work:
We didn't talk about power settings, so now is a good time. Some strobes have power settings that let you tell it "I want a full blast," "I want 1/2 of a full blast," or 1/4, 1/8, etc. The GN of the strobe does depend on the power setting. Similar to the film speed situation, the new GN is the old one times the square root of the power setting. That is, if we set the strobe on 1/2 power, our GN 40 strobe becomes a GN = 40/sqrt(2) = 40/1.4 = 28 strobe. Does that "square root of 2" sound familiar? It should, if you read digression #1. The same reasons behind aperture numbers are behind the guide number changes. If you want the real nitty-gritty on exactly why the power setting affects the guide number only to the square root, read digression #3, where I derive the guide number equation from physical principles. 4. Balancing strobe and ambient lightAll of this theory is great, but how does it help you take pictures with your strobe on manual control?
The goal of exposure control is to get a properly exposed subject and background. You don't want a white-hot overexposed subject on a dark background, and you don't want a colorless, flat subject on an otherwise properly exposed background. What you want is a properly exposed background with just enough strobe light on the subject to restore its color and make it stand out from the background a little. That desire is why you're controlling your strobe manually, so it's about time I show you how to do it. Basically, you have to start with a properly exposed background, and then balance the strobe light against that. So look in your camera's viewfinder after the shot is framed up, and use the meter reading to set your aperture and shutter speed. Mostly you won't get to change the shutter speed very much; it will have to be in the sync range for your camera. It's likely that you'll be stuck in the range between 1/60 and 1/125, or perhaps even down to 1/250 if you have a modern SLR in a housing. So set something reasonable in that range, and then set the aperture to fit the shutter speed and expose the background properly. Then it's time to go to work. You have two options at this point: change your distance to match the strobe's power setting, or change the power setting to match your distance. Obviously, if the picture is framed up just the way you want it, changing distance is not going to work. Most of the time you will adjust the strobe's power setting to match the distance you have selected. This means you have to estimate the strobe-to-subject distance in order to get the right power setting. Even if you change your distance and leave the strobe's power setting alone, you will still have to estimate your distance to the subject in order to get a proper exposure. This skill takes some effort to develop, but everyone can get good at it pretty quickly. If your strobe doesn't have a power setting, you will be forced to change your distance. That's why it's important to have multiple power settings on a strobe. That's one of the reasons I like Ikelite strobes; the SS-200 has 4 power settings: full, 1/2, 1/4, and 1/8. You can almost always find a power setting that will work with the picture. What happens if you realize that the strobe just doesn't have enough power to light your scene at the distance and aperture setting you have chosen? In this case, you have to open up the aperture, which will mean going to a faster shutter speed in order to keep the background exposed properly. Hopefully, your camera will have enough latitude in strobe sync speeds that this is possible. Similarly, if you realize that your strobe's lowest power setting is too powerful, you'll have to stop down to a smaller aperture, which will force a slower (i.e. longer) shutter speed. Again, hopefully your camera will cooperate. It's worth mentioning that the distance that counts is not the lens-to-subject distance, but the strobe-to-subject distance. So if you have your strobe positioned way out away from the camera, be sure to remember that and estimate the distance by looking from strobe to subject, not from you to the subject. |
About | UW Photos | Scuba Picture Uv the Day | Flower Gardens | Aquashot | Trip Reports | RSDiver | Photo Instruction | News | Desktop/Screensaver Images | Site Map |
||